The U.S. Agency for International Development is committed to immunizing people everywhere.
Immunization is cost-effective, slows or halts preventable disease and gives children a healthy start in life. Most importantly, it saves an estimated 2 million to 3 million lives each year, cutting child deaths globally by at least half.
During the last decade, USAID’s child health programs have helped save the lives of more than 9.3 million children, thanks in large part to vaccines.
Since the 2000s, USAID has partnered with Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance to convene public and private sectors to expand access to lifesaving vaccines. The agency has contributed almost $2.8 billion to Gavi since 2001. And that support has helped 73 lower-income countries immunize more than 822 million children and save more than 14 million lives.
USAID’s partnership with Gavi also has helped introduce new vaccines and build sustainable immunization systems to support vaccine distribution.
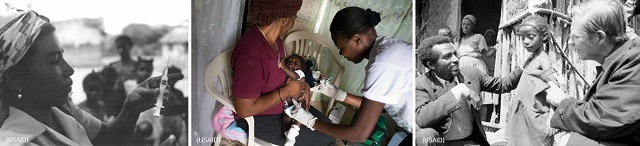
USAID works with host governments and international partners to support immunization programs and deliver safe and effective vaccines to children. (USAID)
A long-term campaign
USAID has combated infectious diseases since its founding in 1961. USAID worked to eradicate smallpox, which in the late 1960s still threatened 60 percent of the world’s population and killed 1 in 4 victims. The U.S. government gave $32 million — the largest contribution — to a worldwide smallpox eradication campaign. Smallpox had plagued humanity for centuries. This effort wiped it out in just 11 years.
In the 1980s, USAID joined the global campaign to fight polio. With partners like the Global Polio Eradication Initiative, USAID helped deliver polio vaccines to children in hard-to-reach places. An estimated 17 million children have been spared childhood paralysis, and polio has been eliminated in more than 120 countries since eradication efforts began in earnest in the mid-1990s.
Available vaccines protect against more than 20 diseases, from pneumonia and cervical cancer to Ebola and measles. USAID continues to support nations’ efforts to develop the efficient and safe immunization policies, strategies and guidelines they need to run their own routine immunization programs.
To fight COVID-19 worldwide, USAID has committed $2 billion, out of a total planned $4 billion, in support of the Gavi COVAX Advance Market Commitment, which aims to provide COVID-19 vaccines for 92 low- and middle-income economies. The contribution will deliver vaccines to the world’s most vulnerable populations and mitigate the spread of COVID-19 and related variants.
For USAID and its partners, vaccines are, and have always been, an important part of the agency’s efforts to save lives, protect people most vulnerable to disease, and promote the stability of communities and nations.
A version of this article was published by USAID. Read the full USAID version here.
Banner image: A child receives a smallpox vaccine. (USAID)







COMMENTS0
LEAVE A COMMENT
TOP